TL;DR
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are unique digital assets on a blockchain. Unlike cryptocurrency tokens that can be exchanged freely for another token of its kind (a bitcoin can be exchanged for any other bitcoin), NFTs can be representations of artworks, gaming items, or documents that exist distinctly by themselves and cannot be replicated, giving them unique values that are determined by many factors such as desirability or collectability.
What are non-fungible tokens (NFTs)?
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are digital assets that also reside on the blockchain. Unlike regular tokens, however, NFTs are made up of unique digital codes that make them distinct from one another. Non-fungibility means that an NFT has certain properties and values that can’t be replaced or interchanged with other tokens.
Think of it like owning a rare trading card or a one-of-a-kind artwork–but in digital form. In fact, most NFTs today are in the art and gaming market, where their individual uniqueness and desirability determine their market value. For instance, in the same way that the appeal of buying antique artwork is being able to have exclusive ownership over a Van Gogh or an Amorsolo, you also have pretty much the same prestige to be able to say you own a “Bored Ape” or a “Cryptopunk”. The privilege is even more obvious in gaming, when owning a unique NFT weapon or vehicle can give you special attributes and even a legendary status within the in-game universe.
But the use cases of NFTs go beyond collectability, and there is a wide range of other applications for this new form of digital asset.
What is ‘fungibility’?
Cryptocurrencies like bitcoin are “fungible” which simply means that one bitcoin is always going to have the same value as another bitcoin and can be freely interchanged or traded with another.
Fiat currencies are also fungible in the sense that if you borrow a one-thousand peso bill from a friend, you can pay it back later with two five-hundred peso bills or ten one-hundred pesos bills regardless of whether the bills are still crinkly or already worn-out since their physical qualities are not perceived to have an effect on their value.
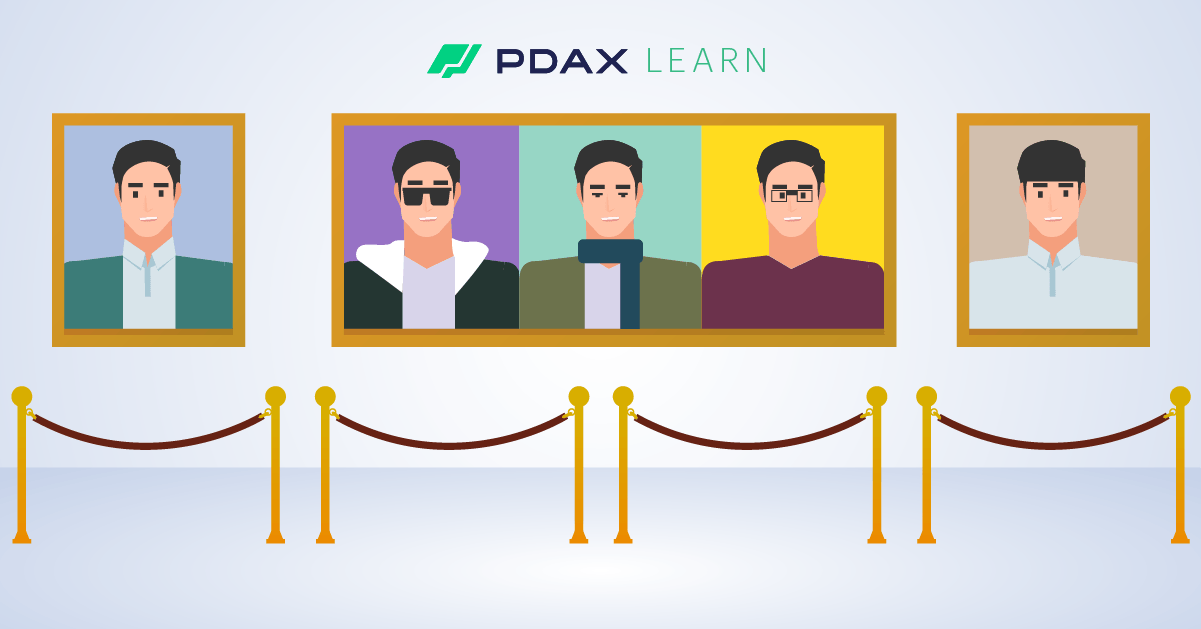
But in the comic book trade, for example, the value of a particular comic will depend on so many factors–rarity, condition, age, popularity, signatures, history of ownership (or even whether a movie version of it is about to be released soon) –all of which have an effect on determining its value. Some comic books will even come with certificates to attest to their authenticity and rarity. Thus you can’t simply just trade one comic book for another–making comic books non-fungible.
So how does the blockchain fit into this? Since a blockchain functions as a decentralized digital ledger system that makes cryptocurrencies immune to ‘double spending’, the same technology can also be used to preserve the uniqueness of NFTs. Simply put, a blockchain prevents anyone from simply making duplicate copies of an NFT since there is an entire global network that maintains a ledger attesting to it as one-of-a-kind and which constantly tracks its ownership.
How do you make NFTs?
Like any other token, NFTs are “minted” onto the blockchain, either through using the decentralized application (dApp) wherein the NFT will be used for such as with gaming NFTs, or on NFT marketplaces when it comes to artworks.
And like any other cryptocurrency transaction, minting NFTs are paid for in “gas fees” to compensate the network’s miners and validators who are providing the computational power for the blockchain. These gas fees are paid for using the particular cryptocurrency of the blockchain where the NFT will be minted on, such as Ether (ETH) for Ethereum-based NFTs or SOL for Solana-based NFTs. Once minted, the existence of your NFT is publicly recorded on the blockchain ledger and can now be viewed in your wallet.
NFTs can become a source of revenue, either through selling them for a profit or getting paid in royalties (for resales of NFT artwork). Some gaming NFTs can even be rented out to other players, or be staked to earn yield within the in-game economy.
What else can NFTs be used for?
Since NFTs are unique assets, their use cases extend well beyond digital trading cards and collectibles. There are already a number of ways in which NFT technology can be used for both virtual and real-world applications:
NFT art - The NFT industry has greatly benefited creators from visual artists to musicians, poets, and filmmakers. With blockchain technology, creators are now able to sell their NFT artworks directly to art aficionados and collectors instead of going through third-party distributors, publishers, or labels, allowing creators to keep most of the profits for themselves.
Records and credentials - Since everyone’s personal records are unique, from birth certificates, and academic credentials to medical records, it makes sense to store such information as NFTs which can be accessed by the individual anywhere at any time. Compared to paper records which can be misplaced, stolen, tampered with, or destroyed in fires or natural disasters, NFT records are also much safer and easier to store.
Real estate - The real estate industry is a prime area for NFT integration. With the use of time-stamped NFTs, proof of ownership, land titles, and property histories are easier to track and can be safeguarded on the blockchain. Self-executing smart contracts can also be used to facilitate sales and transfers of ownership seamlessly without the need for third-party arbitrators to oversee the transaction, drastically saving on fees and time.
The metaverse - Already, we are seeing the beginnings of the metaverse in NFT gaming, where avatars and in-game items such as weapons and vehicles are encoded as NFTs to make the gaming experience unique for every player, as well as to attribute a real sense of ownership over one’s inventory. NFT games also allow for in-game economies to exist as players can trade and sell their NFTs with each other.
But beyond gaming, soon we might be purchasing NFT tickets to attend a live concert on the metaverse. Or, we could be purchasing NFT real estate or “digital land” within a virtual city to set up an online store for selling real-world merchandise. We could even establish corporate offices where employees working remotely can interact with one another with each other’s NFT avatars.
With developers capitalizing on the strengths of the blockchain–such as security, immutability, privacy, and ease of use, it may not be long before the NFT industry is elevated to greater heights and opens up to more industries–benefiting not just the gamers and tech-savvy among us, but even ordinary people as well.
Ready to start with crypto?
Start your trading journey with PDAX.
DISCLAIMER: The statements in this article do not constitute financial advice. PDAX does not guarantee the technical and financial integrity of the digital asset and its ecosystem. Any and all trading involving the digital asset is subject to the user’s risk and discretion and must be done after adequate and in-depth research and analysis.
About PDAX
PDAX is a BSP-licensed exchange where you can trade Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies directly using PHP!
Featured Posts
You might also like
PDAXScope: BTC nears $72K, XRP breakout watch
PDAX
March 13, 2026
Bitcoin rallies, DOGE jumps 15%, HYPE may retest
PDAX
March 06, 2026
PDAXScope: Circle posts USDC earnings, BTC ETFs draw $506M
PDAX
February 27, 2026
PDAXScope: Crypto market today: ETH eyes $2.5K, BTC at $69K
PDAX
February 20, 2026